BCLPemerging.com
PFAS Update: State-by-State Groundwater Regulations, May 2023
May 04, 2023This blog was originally published in April 2023. Visit our up-to-date blog on PFAS in groundwater: state-by-state regulations >
In the absence of federal cleanup standards for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (“PFAS”) in groundwater, numerous states have started the process of regulating PFAS in groundwater themselves. As a result, states have adopted a patchwork of regulations and guidance standards that present significant compliance challenges to impacted industries. This client alert explores the current landscape of state regulations regarding the guidance, notification, and cleanup levels for PFAS – typically perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (“PFOS”) and perfluorooctanoic acid (”PFOA”) – in groundwater.
Federal Interim Remedial Guidance
Although no legally binding standards for groundwater have been issued at the federal level, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (“EPA”) has issued an influential document: Interim Recommendations to Address Groundwater Contaminated with PFOA and PFOS. The key details are:
- Date: Implemented on December 19, 2019.
- Site Applicability: All locations that are currently undergoing federal cleanup actions.
- Recommendations:
- Apply a screening level of 40 ppt for PFOA and PFOS, individually or combined, to determine if the compounds are present at a site and may justify additional actions.
- Apply EPA’s 2016 Drinking Water Health Advisory of 70 ppt for PFOA and PFOS, individually or combined (“HA”) as the preliminary remediation goal for contaminated groundwater that is a current or potential source of drinking water.
On February 3, 2023, EPA stated that it was currently in the process to update these recommendations, which is not surprising given its recent revisions to the PFAS HAs, but as of the date of this publication no revised policy is available.
State Regulations
The snapshot provided below is current as of May 2, 2023 but it is important to note that this is a developing regulatory space. Some states, such as Rhode Island, have proposed revised groundwater regulations for various PFAS substances that may take effect soon.
Businesses should consider whether they currently use or discharge any PFAS compounds, and if so, evaluate if any state regulations apply, particularly if they operate in any of the below-listed jurisdictions. In addition, owners of property with legacy PFAS use, and prospective purchasers of commercial and industrial properties, should review the most current groundwater quality standards as part of the due diligence process.
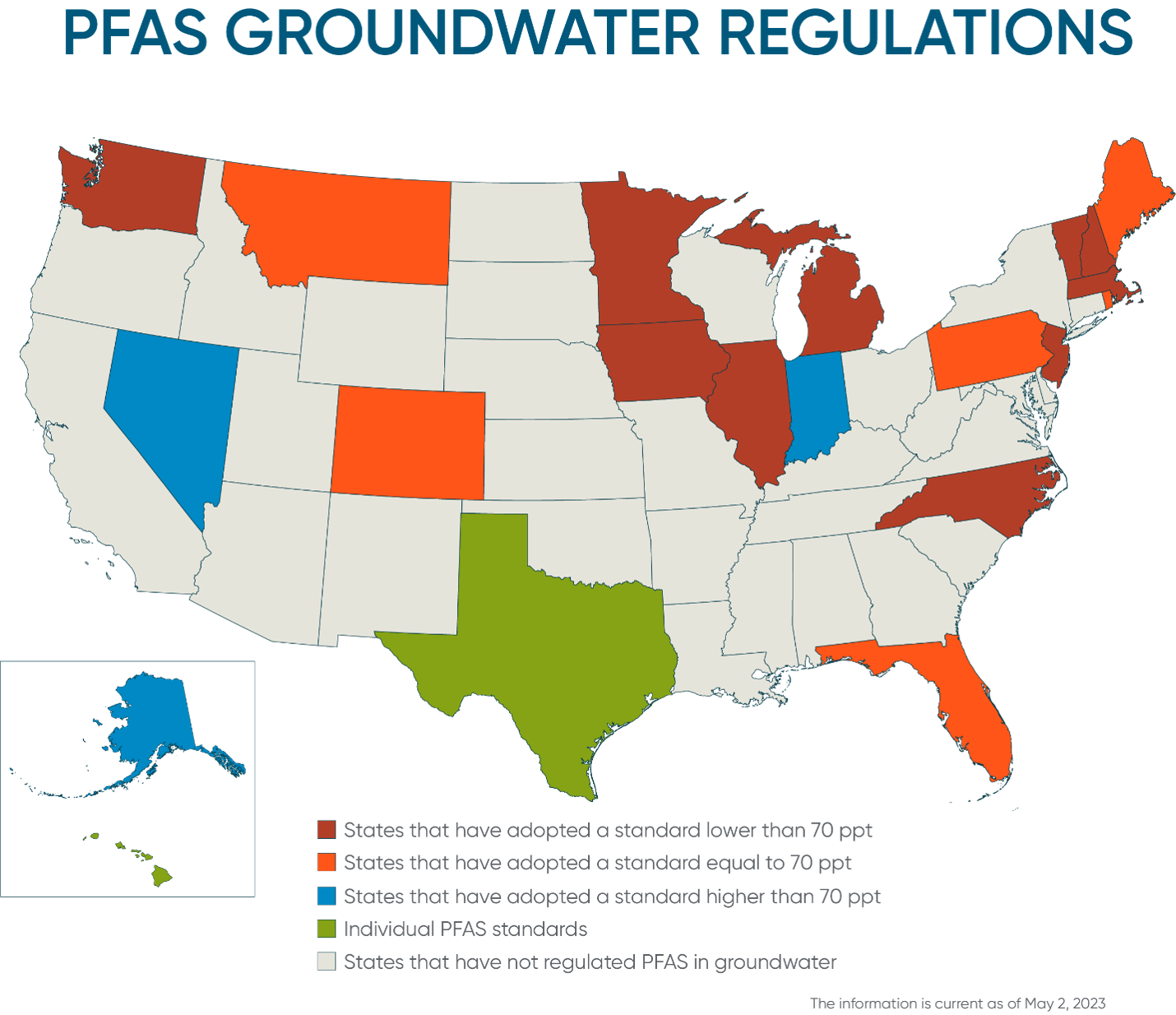
States that have adopted a standard lower than 70 ppt |
Concentration Level
2 ppt (stated by the Illinois Pollution Control Agency as 2 ng/L)
Type of Regulation
PFOA (Guidance)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
14 ppt (stated by the Illinois Pollution Control Agency as 14 ng/L)
Type of Regulation
PFOS (Guidance)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
21 ppt (stated by the Illinois Pollution Control Agency as 21 ng/L)
Type of Regulation
PFNA (Guidance)
Information
Concentration Level
0.004 ppt for protected groundwater sources (stated by the Iowa Department of Natural Resources as 0.000000004 mg/L)
Type of Regulation
PFOA (Advisory)
Information
Concentration Level
0.02 ppt for protected groundwater sources (stated by the Iowa Department of Natural Resources as 0.00000002 mg/L)
Type of Regulation
PFOS (Advisory)
Information
Concentration Level
21 ppt for protected groundwater sources (stated by the Iowa Department of Natural Resources as 0.000021 mg/L)
Type of Regulation
PFNA (Advisory)
Information
Concentration Level
20 ppt (stated in the regulation as .02 ppb)
Type of Regulation
6 PFAS Substances combined: PFOA, PFOS, PFHxS, PFNA, PFHpA, and PFDA (Clean Up)
Information
Concentration Level
6 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFNA (Clean Up)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
8 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFOA (Clean Up)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
16 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFOS (Clean Up)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
51 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFHxS (Clean Up)
Information
Concentration Level
15 ppt (stated by the Minnesota Department of Health as 0.015 ppb)
Type of Regulation
PFOS (Guidance)
Information
Health Advisory Level and Related Information
Concentration Level
35 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFOA (Advisory)
Information
Health Advisory Level (see page 181) and Related Information
Concentration Level
47 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFHxS (Advisory)
Information
Health Advisory Level (see page 180) and Related Information
Concentration Level
11 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFNA (Clean Up)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
12 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFOA (Clean Up)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
15 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFOS (Clean Up)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
18 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFHxS (Clean Up)
Information
Concentration Level
2 ppt (stated by the regulation as 0.002 µg/L)
Type of Regulation
Chloroperfluoropolyether carbonates[1] (Clean Up)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
13 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFNA and PFOS (Clean Up)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
14 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFOA (Clean Up)
Information
Concentration Level
0.004 ppt (stated by the North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality as a value below the practical quantification limit, or PQL)
Type of Regulation
PFOA (Advisory)
Information
Concentration Level
20 ppt (stated in the regulation as .02 µg/L)
Type of Regulation
5 PFAS substances combined: PFHpA, PFHxS, PFNA, PFOS and PFOA (Notification)
Information
Concentration Level
9 ppt (stated by the Washington Department of Ecology as 9 ng/L)
Type of Regulation
PFNA (Guidance)
Information
Concentration Level
10 ppt (stated by the Washington Department of Ecology as 10 ng/L)
Type of Regulation
PFOA (Guidance)
Information
Concentration Level
15 ppt (stated by the Washington Department of Ecology as 15 ng/L)
Type of Regulation
PFOS (Guidance)
Information
Concentration Level
24 ppt (stated by the Washington Department of Ecology as 24 ng/L)
Type of Regulation
HFPO-DA or GenX (Guidance)
Information
Concentration Level
65 ppt (stated by the Washington Department of Ecology as 65 ng/L)
Type of Regulation
PFHxS (Guidance)
Information
States that have adopted a standard equal to 70 ppt |
Concentration Level
70 ppt
Type of Regulation
Site-specific Standard for PFOA and PFOS (Clean Up)
Information
Concentration Level
70 ppt
Type of Regulation
Follow the EPA Health Advisory Level: PFOS and PFOA combined (Guidance and Notification)
Information
Concentration Level
70 ppt
Type of Regulation
Follow the EPA Health Advisory Level: PFOS and PFOA combined (Guidance and Notification)
Note: Maine has both residential and construction standards
Information
Maximum Exposure Guideline (see pages 36 and 60) and Related Information
PFOS + PFOA + PFHpA + PFNA + PFHxS < 70 ppt
Concentration Level
70 ppt
Type of Regulation
Follow the EPA Health Advisory Level: PFOS and PFOA combined (Guidance and Notification)
Information
Numeric Water Quality Standard (page 60) and Related Information
Concentration Level
70 ppt
Type of Regulation
Follow the EPA Health Advisory Level: PFOS and PFOA combined (Guidance and Notification)
Information
Concentration Level
70 ppt
Type of Regulation
Follow the EPA Health Advisory Level: PFOS and PFOA combined (Guidance and Notification)
Information
States that have adopted a standard higher than 70 ppt |
Concentration Level
400 ppt (stated in the regulation as 0.4 µg/L)
Type of Regulation
PFOA and PFOS separately (Clean Up)
Information
Concentration Level
140 ppt (stated by the Illinois Pollution Control Agency as 140 ng/L)
Type of Regulation
PFHxS (Guidance)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
2,100 ppt (stated by the Illinois Pollution Control Agency as 2,100 ng/L)
Type of Regulation
PFBS (Guidance)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
560,000 ppt (stated by the Illinois Pollution Control Agency as 560,000 ng/L)
Type of Regulation
PFHxA (Guidance)
Information
Concentration Level
400,000 ppt (stated in the regulation as 400 µg/L)
Type of Regulation
PFBS (Guidance)
Information
Concentration Level
140 ppt for protected groundwater sources (stated by the Iowa Department of Natural Resources as 0.00014 mg/L)
Type of Regulation
PFHxS (Advisory)
Information
Concentration Level
2,000 ppt for protected groundwater sources (stated by the Iowa Department of Natural Resources as 0.02 mg/L)
Type of Regulation
PFBS (Advisory)
Information
Concentration Level
400,000 ppt (stated in the regulation as 400 ppb)
Type of Regulation
PFBS (Guidance)
Note: Maine has both residential and construction standards
Information
Maximum Exposure Guideline (see page 60)
Concentration Level
370 ppt
Type of Regulation
HFPO-DA (Clean Up)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
420 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFBS (Clean Up)
Information
Regulation and Related Information
Concentration Level
400,000 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFHxA (Clean Up)
Information
Concentration Level
2,000 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFBS (Guidance)
Information
Health Advisory Level (see page 180) and Related Information
Concentration Level
7,000 ppt
Type of Regulation
PFBA (Advisory)
Information
Health Advisory Level (see page 180) and Related Information
Concentration Level
667 ppt (stated in the regulation as 0.667 µg/L)
Type of Regulation
PFOS and PFOA (Guidance)
Information
Basic Comparison Levels and Related Information
Concentration Level
667,000 ppt (stated in the regulation as 667 µg/L)
Type of Regulation
PFBS (Guidance)
Information
Concentration Level
10,000 ppt (stated in the regulation as 10 µg/L)
Type of Regulation
PFBS Residential Property (Clean Up)
Information
Medium-Specific Concentration Standards and Related Information
Concentration Level
29,000 ppt (stated in the regulation as 29 µg/L)
Type of Regulation
PFBS Non-residential Property (Clean Up)
Information
Medium-Specific Concentration Standards and Related Information
Concentration Level
345 ppt (stated by the Washington Department of Ecology as 345 ng/L)
Type of Regulation
PFBS (Guidance)
Information
Individual PFAS standards |
Concentration Level
40 ppt, etc.
Type of Regulation
PFOA and PFOS; 17 other PFAS substances (Advisory) including the following: PFNA and PFDA (.004 µg/L); PFUnDA (.01 µg/L); PFDoDA and PFTrDA (.013 µg/L); PFHxS (.019 µg/L); PFHpS and PFDS (.02 µg/L); PFOSA (.024 µg/L); PFTeDA (.13 µg/L); HFPO-DA (.16 µg/L); PFHpA (0.4 µg/L); PFBS (.6 µg/L); 6:2 FTS (.78 µg/L); PFPeA (.8 µg/L); PFHxA (4.0 µg/L ); and PFBA (7.6 µg/L).
Information
Environmental Action Levels (see page 48)
Concentration Level
290 ppt, etc.
Type of Regulation
16 Different PFAS Substances (Clean Up)
Texas has 15 additional regulations, including the following: PFHxS, PFHxA, and PFPeA (93 ppt); PFNA, PFDS, PFUnA, PFOSA, PFTrDA, PFTeA, and PFDoA (290 ppt); PFDA (370 ppt); PFOS and PFHpA (560 ppt); PFBS (34,000 ppt); and PFBA (71,000 ppt). A reader-friendly summary of these limitations can be found at a publication from the Reese Air Force Base.
Information
Protective Concentration Levels (see March 2022 Tier 1 PCL Table)
Related information |
*at date of publication
- Alabama
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maryland
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Nebraska
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Dakota
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Ohio
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Utah
- Virginia
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
Notification
A corporate representative must inform the appropriate state official that the groundwater is above the stated limit.
Guidance
These levels are not binding limits, but they can serve as the basis for regulatory action, and are a useful tool for due diligence and risk assessment.
Clean-Up
Investigation and remediation is usually required when concentration levels exceed the clean-up threshold. This is usually expressed by groundwater quality standards that identify specific clean-up criteria.
Additional Information
Without federal PFAS standards for groundwater, states have enacted a wide range regulatory concentration levels. For example, for PFAS substances in groundwater, one of the most stringent concentration is 0.004 ppt (Iowa; PFOA only) and the most lenient concentration is 667,000 ppt (Nevada; PFBS only). The following chart demonstrates that even for PFOA and PFOS, which have been more extensively studied and regulated, there is still a wide discrepancy in the values that different states have adopted.
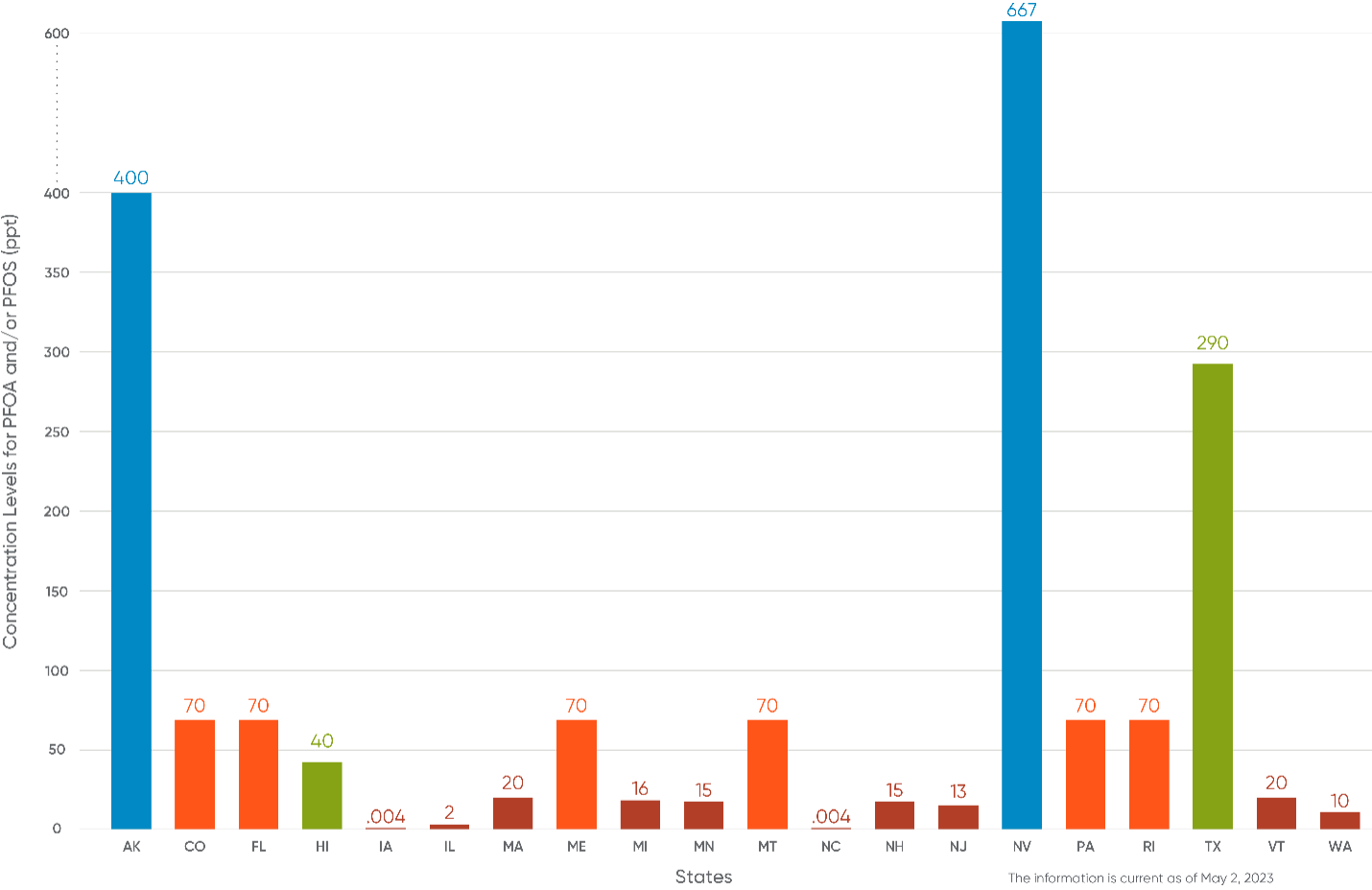
Conclusion
Businesses operating in the 20 states where groundwater regulations have already been enacted should consider whether they currently use or discharge any of the regulated PFAS compounds. In addition, owners of property with legacy PFAS use, and prospective purchasers of commercial and industrial properties in these jurisdictions will increasingly need to incorporate the groundwater quality standards as part of their due diligence processes.
For more information on PFAS chemicals, and the regulatory and litigation risks that they pose, please visit our PFAS webpage. If you have a question about how to manage PFAS risk in any jurisdiction, contact Tom Lee, John Kindschuh, Emma Cormier, or any other member of our PFAS team at Bryan Cave Leighton Paisner LLP.
Related Practice Areas
-
PFAS Team
-
Environment





