BCLPemerging.com
PFAS in Soil: State Regulations
Updated: February 2025
Feb 04, 2025Summary
In the absence of enforceable federal standards for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (“PFAS”) in soil, several states have started the process of regulating PFAS in soil themselves. These regulations have implications for due diligence, site investigations, and remediation decisions. This client alert explores the current landscape of state regulations regarding the advisory, notification, and cleanup levels for PFAS – most commonly perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (“PFOS”) and perfluorooctanoic acid (”PFOA”) – in soil.
Federal Regional Screening Levels
The United States Protection Agency (“EPA”) has issued Regional Screening Levels (“RSLs”) for numerous PFAS substances, and the levels for some of the most commonly regulated PFAS compounds are listed below. RSLs are advisory levels and are not enforceable limits, but both EPA and state agencies often use RSLs to investigate and characterize potential remediation sites.
Residential soil level (mg/kg)[1]
0.0063
Industrial soil level (mg/kg)[2]
0.058
Residential soil level (mg/kg)[1]
0.000019
Industrial soil level (mg/kg)[2]
0.000078
Residential soil level (mg/kg)[1]
0.19
Industrial soil level (mg/kg)[2]
2.5
Residential soil level (mg/kg)[1]
0.23
Industrial soil level (mg/kg)[2]
3.5
Residential soil level (mg/kg)[1]
1.3
Industrial soil level (mg/kg)[2]
16
Residential soil level (mg/kg)[1]
19
Industrial soil level (mg/kg)[2]
250
Residential soil level (mg/kg)[1]
32
Industrial soil level (mg/kg)[2]
410
Residential soil level (mg/kg)[1]
78
Industrial soil level (mg/kg)[2]
1,200
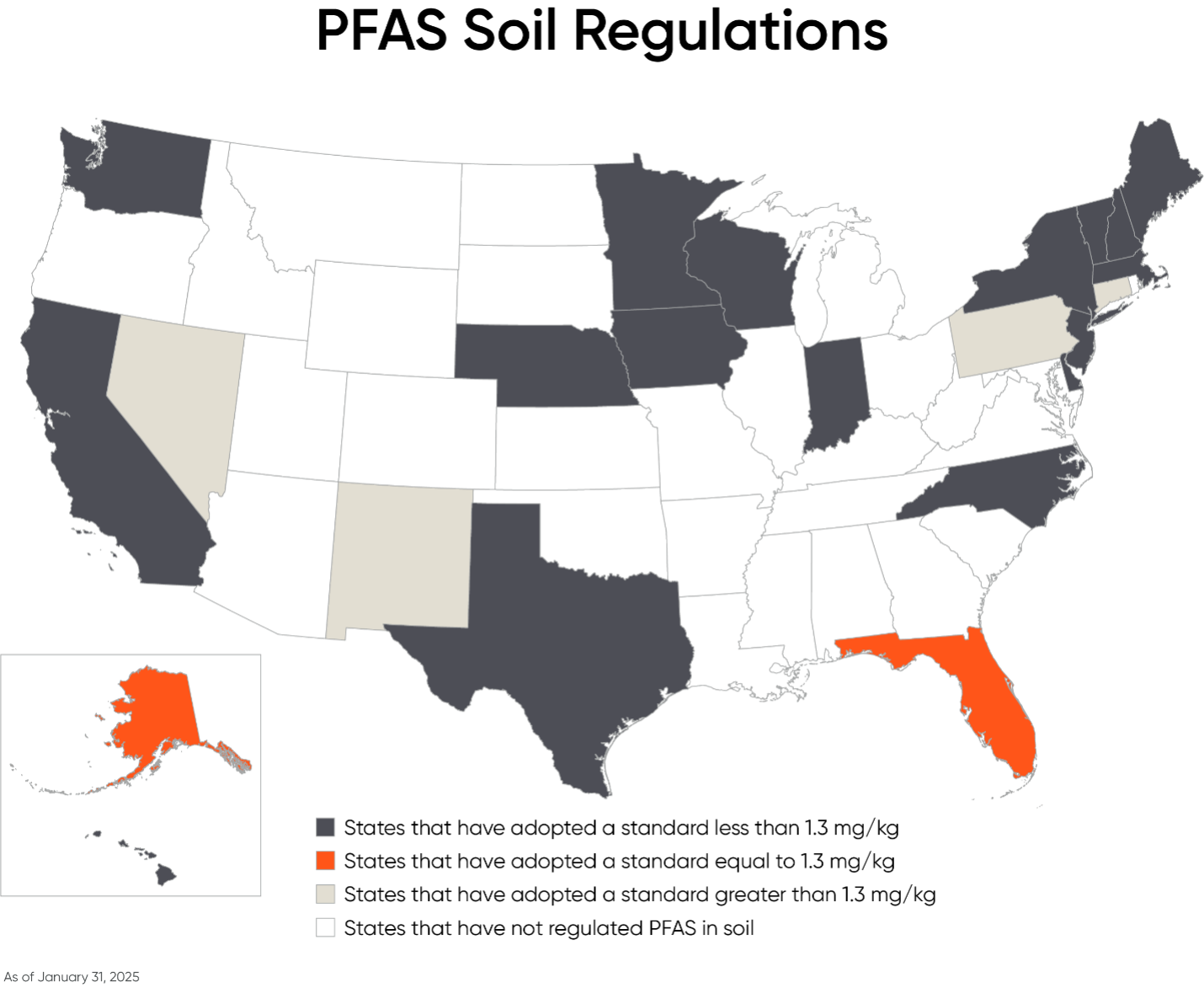
State Regulations
The information provided below is current as of January 31, 2025, but it is important to note that this is a developing regulatory space. There are some proposed laws, in states such as Massachusetts, that address PFAS soil permitting or remediation issues, so additional legislation on this topic may be enacted later this year.
Concentration Level
PFOA and PFOS
- Arctic zone: 2.2 mg/kg
- Under 40 inch zone: 1.6 mg/kg
- Over 40 inch zone: 1.3 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Clean up
Information
Regulation (See 18 AAC 75, Table B-1)
Concentration Level
PFOA
-
Resident non-cancer hazard: 0.028 mg/kg
-
Commercial/industrial non-cancer hazard: 0.37 mg/kg
-
Construction worker non-cancer hazard: 0.086 mg/kg
PFOS
- Resident non-cancer hazard: 0.11 mg/kg
- Commercial/industrial nonconcern hazard: 1.5 mg/kg
- Construction worker non-cancer hazard: 0.34 mg/kg
Note: There are also cancer risk standards for all three of these categories
Type of regulation
Screening level advisory
Information
San Francisco Bay Regional Water Quality Control Board Interim Final Environmental Screening Levels (page 12; currently in the process of updating standards)
Concentration Level
PFOA + PFOS + PFNA + PFHxS + PFHpA = 1.35 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Clean up
Information
Remediation standard regulations, residential direct exposure criteria (Table 2, pgs. 130-131)
Concentration Level
- PFOA: 0.0002 mg/kg
- PFOS: 0.0063 mg/kg
- HFPO-DA: 0.023 mg/kg
- PFNA: 0.19 mg/kg
- PFHxS: 1.3 mg/kg
- PFDoDA: 3.2 mg/kg
- TFSI: 23 mg/kg
- PFBS and PFUDA: 19 mg/kg
- PFHxA: 32 mg/kg
- PFPrA; 39 mg/kg
- PFTetDA: 63 mg/kg
- PFBA: 78 mg/kg
- PFODA: 2,500 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Notification
Information
Hazardous Substance Cleanup Act Reporting Level Table (see Appendix A, pages 10-11)
Concentration Level
PFOS and PFOA
- Residential: 1.3 mg/kg
- Commercial/industrial: 25 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Screening level/advisory
Information
PFAS Dynamic Plan (see page 9)
Concentration Level
PFOS and PFOA
- 0.025 mg/kg[3]
Type of regulation
Screening level/advisory
Information
Environmental Action Levels (see table A-1)
Concentration Level
- PFOS: 0.2 mg/kg
- PFNA and PFOA: 0.3 mg/kg
- PFHxS: 2 mg/kg
- PFDoDA: 4 mg/kg
- PFOA: 5 mg/kg
- PFBS and PFUDA: 30 mg/kg
- PFHxA: 40 mg/kg
- PFTetA: 90 mg/kg
- PFODA: 4,000 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Screening Level/Advisory
Information
Concentration Level
- PFDA: 0.00016 mg/kg
- PFOS: 0.00048 mg/kg
- PFNA: 0.18 mg/kg
- PFHxS: 1.6 mg/kg
- PFBS: 18 mg/kg
- PFOA: 35 mg/kg
- PFHxA: 39 mg/kg
- PFBA: 61 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Screening level/advisory
Information
Concentration Level
PFOA
- Residential: 0.26 mg/kg
- Commercial worker: 3.4 mg/kg
- Construction worker: 0.77 mg/kg
PFOS
- Residential: 0.17 mg/kg
- Commercial worker: 2.2 mg/kg
- Construction worker: 0.51 mg/kg
PFBA
- Residential: 110 mg/kg
- Commercial worker: 1,600 mg/kg
- Construction worker: 2,000 mg/kg
PFBS
- Residential: 26 mg/kg
- Commercial worker: 340 mg/kg
- Construction worker: 230 mg/kg
PFHxS
- Residential: 1.7 mg/kg
- Commercial worker: 22 mg/kg
- Construction worker: 5.1 mg/kg
PFHxA
- Residential: 43 mg/kg
- Commercial worker: 560 mg/kg
- Construction worker: 130 mg/kg
PFNA
- Residential: 0.26 mg/kg
- Commercial worker: 3.4 mg/kg
- Construction worker: 0.77 mg/kg
Note: There are three other categories listed, such as ”Leaching to Groundwater,” “Park User,” and “Recreator Sediment”
Type of regulation
Screening level/advisory
Information
Remedial Action Guidelines (pg. 65)
Concentration Level
- 0.3 mg/kg (stated in the regulation as 0.3 ppm) for SW-1
- 6 PFAS substances combined: PFOA, PFOS, PFHxS, PFNA, PFHpA, and PFDA
- Note: the concentration level depends on the soil classification designation
Type of regulation
Clean up
Information
Regulation (see Table 5) and MassDEP related information
Concentration Level
PFOS (stated in the blueprint in ng/g)
-
Residential: 0.041 mg/kg
-
Non-residential: 0.56 mg/kg
PFHxS
-
Residential: 0.13 mg/kg
-
Non-residential: 1.7 mg/kg
PFOA
- Residential: 0.24 mg/kg
- Non-residential: 3.2 mg/kg
PFBA
- Residential: 38 mg/kg
- Non-residential: 520 mg/kg
PFBS
- Residential: 57 mg/kg
- Non-residential: 77 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Screening level/advisory
Information
PFAS Blueprint (see pgs. 180-182)
Concentration Level
PFOA
-
Residential: 0.32 mg/kg
-
Industrial: 1.5 mg/kg
PFOS
-
Residential: 3.2 mg/kg
-
Industrial: 150 mg/kg
Note: This is only for the Voluntary Cleanup Program
Type of regulation
Screening level/advisory
Information
Regulation (see table A-1)
Concentration Level
PFOA:
- Residential: 2.35 mg/kg
- Indoor industrial/commercial worker: 70.1 mg/kg
- Outdoor industrial/commercial worker: 38.9 mg/kg
PFOS:
- Residential: 1.56 mg/kg
- Indoor industrial/commercial worker: 46.7 mg/kg
- Outdoor industrial/commercial worker: 26 mg/kg
PFBS
- Residential: 19 mg/kg
- Indoor industrial/commercial worker: 701 mg/kg
- Outdoor industrial/commercial worker: 274 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Screening level/advisory
Information
Concentration Level
PFOS
- Residential: 0.1 mg/kg
- Non-residential: 0.6 mg/kg
PFHxS and PFNA
- Residential: 0.1 mg/kg
- Non-residential: 0.9 mg/kg
PFOA
- Residential: 0.2 mg/kg
- Non-residential: 1.3 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Screening level/advisory
Information
Environmental Health Program direct contact risk-based soil concentrations
Proposed Soil Remediation Standards
Concentration Level
PFNA
- Residential: 0.047 mg/kg
- Non-residential: 0.67 mg/kg
PFOS
- Residential: 0.11 mg/kg
- Non-residential: 1.6 mg/kg
PFOA
- Residential: 0.13 mg/kg
- Non-residential: 1.8 mg/kg
HFPO-DA or GenX
- Residential: 0.23 mg/kg
- Non-residential: 3.9 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Clean up
Information
Interim soil remediation standards and NJDEP related information
Concentration Level
PFOS, PFOA, and PFHxS
- Residential: 1.56 mg/kg
- Industrial/occupational: 260 mg/kg
- Construction worker: 7.08 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Screening level/advisory
Information
Soil Screening Guidance for Human Health Risk Assessments (see Table A-1)
Concentration Level
PFOA (stated in the document in ppb)
- Residential: 0.0066 mg/kg
- Commercial: 0.5 mg/kg
- Industrial: 0.6 mg/kg
PFOS
- Residential: 0.0088 mg/kg
- Commercial: 0.44 mg/kg
- Industrial: 0.44 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Screening level/advisory
Information
New York Department of Environmental Conservation Sampling, Analysis, and Assessment of PFAS (see pg. 3)
Concentration Level
PFOS
- Residential: 0.025 mg/kg
- Industrial: 0.33 mg/kg
PFHxS
- Residential: 0.25 mg/kg
- Industrial: 3.3 mg/kg
PFOA
- Residential: 0.038 mg/kg
- Industrial: 0.49 mg/kg
PFNA
- Residential: 0.038 mg/kg
- Industrial: 0.49 mg/kg
Ammonium perfluoro-2-methyl-3-oxahexanoate
- Residential: 0.038 mg/kg
- Industrial: 0.49 mg/kg
HFPO-DA (GenX)
- Residential: 0.047 mg/kg
- Industrial: 0.7 mg/kg
PFBS
- Residential: 3.8 mg/kg
- Industrial: 49 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Screening level/advisory
Information
Concentration Level
PFOA and PFOS
- Residential: 4.4 mg/kg
- Non-residential: 64 mg/kg
PFBS
- Residential: 66 mg/kg
- Non-residential: 960 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Clean up
Information
Concentration Level
PFOA
- 0.5 acre source area: 0.6 mg/kg
- 30 acre source area: 0.49 mg/kg
PFOS
- 0.5 acre source area: 1.5 mg/kg
- 30 acre source area: 1.5 mg/kg
- 16 different PFAS substances[4]
Type of regulation
Clean up
Information
Protective Concentration Levels, see May 2023 tier 1 PCL table; residential (table 1) and commercial (table 2)
Concentration Level
PFOS
- Residential: 0.12 mg/kg
- Commercial: 1.4 mg/kg
PFOA
Residential: 0.18 mg/kg
Commercial: 2.2 mg/kg
PFNA
- Residential: 0.18 mg/kg
- Commercial: 2.2 mg/kg
PFHxS
- Residential: 1.12 mg/kg
- Commercial: 14 mg/kg
PFBS
- Residential: 18 mg/kg
- Commercial: 215 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Screening Level/Advisory
Information
Vermont Department of Health publication (see Attachment 1)
Concentration Level
PFDA: 0.00016 mg/kg
PFOA: 0.0024 mg/kg
PFOS: 0.008 mg/kg
PFNA: 0.2 mg/kg
HFPO-DA (GenX): 0.24 mg/kg
PFHxS: 0.78 mg/kg
Fluroelomer Sulfonic Acid (6:2 FTS): 16 mg/kg
PFBS: 24 mg/kg
PFHxA: 40 mg/kg
PFBA: 80 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Screening level/advisory
Information
Washington Department of Ecology Toxics Cleanup Program Publication (pgs. 10, 11, and 13)
Concentration Level
PFOA and PFOS
- Residential: 1.26 mg/kg
- Industrial: 16.4 mg/kg
Type of regulation
Clean up
Information
No enacted PFAS soil regulations (as of the date of publication):
- Alabama
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- Colorado
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maryland
- Michigan
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Utah
- Virginia
- West Virginia
- Wyoming
Key
Notification: A corporate representative must inform the appropriate state official that the soil concentration is above the stated limit.
Screening level/advisory: These levels are not binding limits, but they can serve as the basis for regulatory action, and are a useful tool for due diligence and risk assessment.
Clean up: Investigation and remediation is usually required when concentration levels exceed the clean up threshold. This is usually expressed by soil concentration standards that identify specific clean up criteria.
Analysis
Perhaps the most remarkable thing about the different state regulations regarding PFAS in soil is the wide range of regulated concentration levels. For example, Iowa regulates PFOS at 0.00048 mg/kg, while Pennsylvania regulates PFOS at 4.4 mg/kg for residential property uses (64 mg/kg for non-residential). Some of these discrepancies are driven by the different compounds being regulated, but to control for some of those variables, the following chart illustrates the discrepancies in the concentration levels solely for PFOA and/or PFOS.
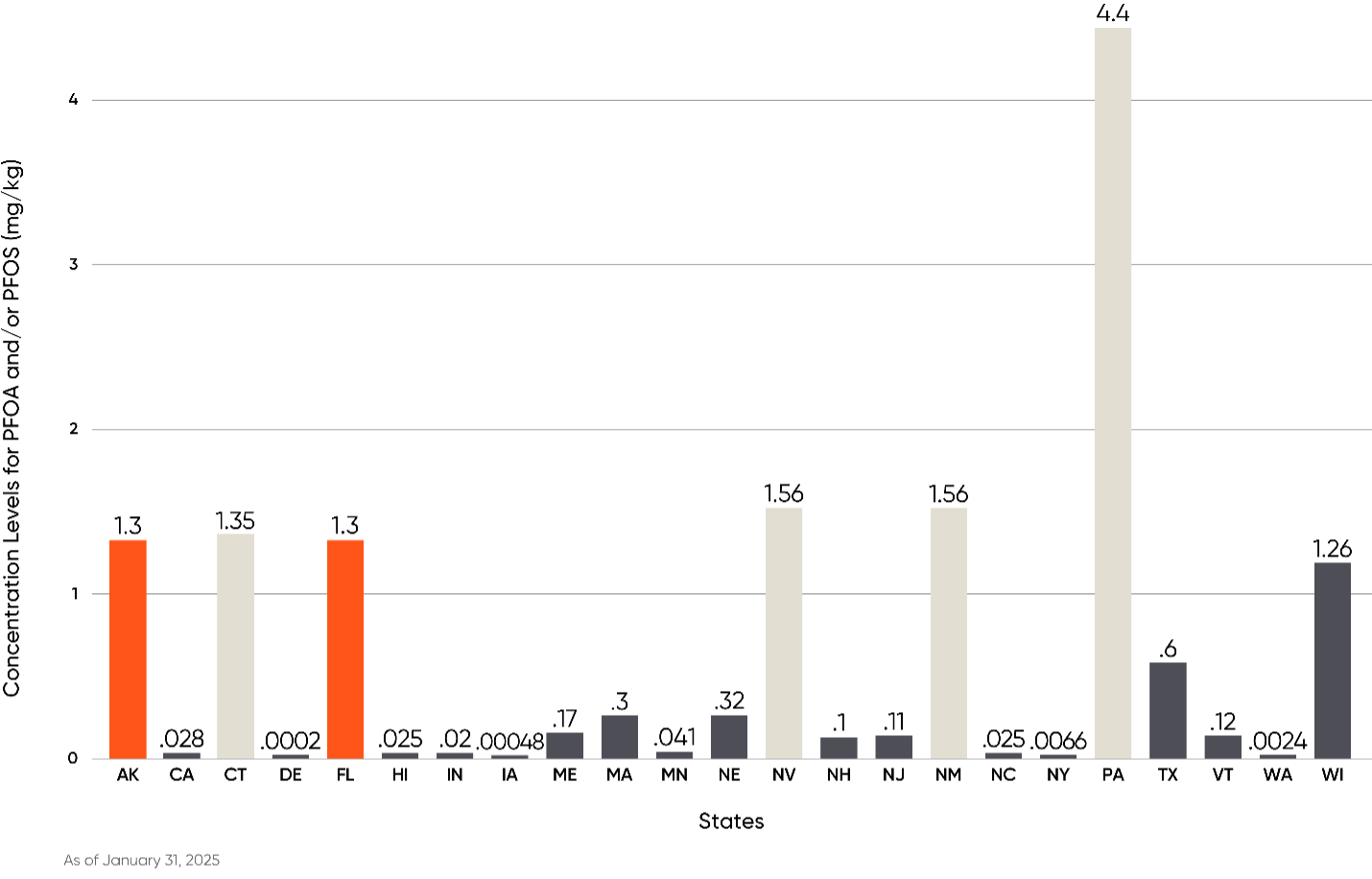
Notably, there are substantial differences in the regulatory concentrations (sometimes measured by orders of magnitude) for the same compounds across the different states. This variably presents obvious diligence and compliance challenges for businesses that buy, sell, and operate properties across the country, and which may need to engage with regulators on future site investigation and remediation projects.
Conclusion
Businesses operating in the states where soil regulations have been enacted should consider whether they currently use or discharge any of the regulated PFAS compounds into the soil or have done so in the past. In addition, prospective purchasers of commercial and industrial properties in these jurisdictions will increasingly need to incorporate the soil contamination standards as part of their due diligence processes to underwrite the potential risk of future regulatory action.
For more information on PFAS chemicals, and the regulatory and litigation risks that they pose, please visit our PFAS webpage. If you have a question about how to manage PFAS risk in any jurisdiction, contact Tom Lee, Bryan Keyt, Erin Brooks, John Kindschuh, or any other member of our PFAS team at BCLP.
[1] See the “Resident Soil” screening table (orange column).
[2] See the “Industrial Soil” screening table (orange column).
[3] Hawaii has regulated additional PFAS compounds: PFDA (.0025 mg/kg); PFNA (.0028 mg/kg); PFHxS (.0038 mg/kg); PFUnDA (.0063 mg/kg); PFHpS (.0079 mg/kg); PFDoDA and PFTrDA (.0084 mg/kg); PFOSA (.015 mg/kg); PFHpA (.025 mg/kg); PFTeDA (.084 mg/kg); PFPeS (.1 mg/kg); PFBS (.16 mg/kg); PFPeA (.51 mg/kg); PFHxA (2.5 mg/kg); PFBA (4.8 mg/kg).
[4] Residential soil limits (not commercial) in Texas are as follows: PFOSA: .5 acre source area -- 0.058 mg/kg and 30 acre source area: 0.031 mg/kg; PFHxS: .5 acre source area -- 0.25 mg/kg and 30 acre source area -- 0.24 mg/kg; PFTeDA: 0.5 and 30 acre source area -- 0.51 mg/kg; PFTrDA: .5 and 30 acre source area -- 0.61 mg/kg; PFNA: .5 acre source area -- 0.76 mg/kg and 30 acre source area: 0.73 mg/kg;PFDoA: .5 acre source area -- 0.79 mg/kg and 30 acre source area -- 0.78 mg/kg; PFDS and PFUnDA: .5 and 30 acre source area -- 0.8 mg/kg; PFDA: .5 acre source area -- 0.99 mg/kg and 30 acre source area -- 0.98 mg/kg; PFHpA: .5 and 30 acre source area – 1.5 mg/kg; PFPeA and PFHxA .5 and 30 acre source area – 33 mg/kg; PFBA: .5 acre source area -- 61 mg/kg and 30 acre source area -- 56 mg/kg; PFBS: .5 acre source area -- 86 mg/kg and 30 acre source area: 80 mg/kg.
Related Practice Areas
-
PFAS Team
-
Environment
-
ESG Governance, Compliance & Reporting






